Cervical Spine Surgery & Disc Replacement
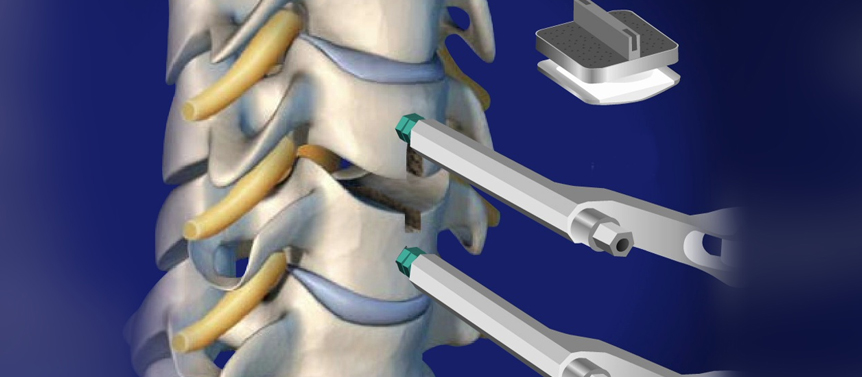
Cervical spine surgery and disc replacement refer to surgical procedures performed on the cervical (neck) region of the spine to treat specific conditions affecting the intervertebral discs. The cervical spine consists of the seven vertebrae (C1 to C7) located in the neck region. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai
Cervical disc replacement surgery aims to address conditions such as cervical disc herniation, degenerative disc disease, or cervical radiculopathy (nerve compression) by replacing the damaged or diseased disc with an artificial disc implant. This procedure is also known as cervical total disc replacement or cervical arthroplasty.
During cervical disc replacement surgery, the surgeon typically follows these steps:
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the front of the neck to access the cervical spine.
- Removal of the damaged disc: The surgeon removes the damaged or diseased disc, taking care not to disturb the nearby nerves and blood vessels.
- Placement of the artificial disc: The surgeon inserts an artificial disc implant between the adjacent vertebral bodies, restoring disc height and potentially preserving motion in the cervical spine. The artificial disc is designed to mimic the function and structure of a natural disc.
- Closure: The incision is closed using sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to the surgical site.
Cervical disc replacement surgery offers potential advantages over traditional cervical fusion surgery, which involves fusing the affected vertebrae together. These advantages include:
- Preservation of motion: Disc replacement surgery aims to maintain or restore motion in the cervical spine, potentially reducing stress on adjacent discs and the risk of adjacent segment degeneration.
- Maintenance of neck flexibility: By preserving motion, patients may have improved range of motion and flexibility in the neck compared to fusion.
- Potentially reduced risk of complications: There may be a lower risk of certain complications associated with fusion surgery, such as adjacent segment disease and pseudoarthrosis (failed fusion).
However, it's important to note that not all patients or conditions are suitable for cervical disc replacement surgery. The decision to undergo this procedure is made on an individual basis, taking into account factors such as the patient's specific condition, the extent of disc damage, spinal stability, and the expertise of the surgeon. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai
Endoscopic Spine Surgery
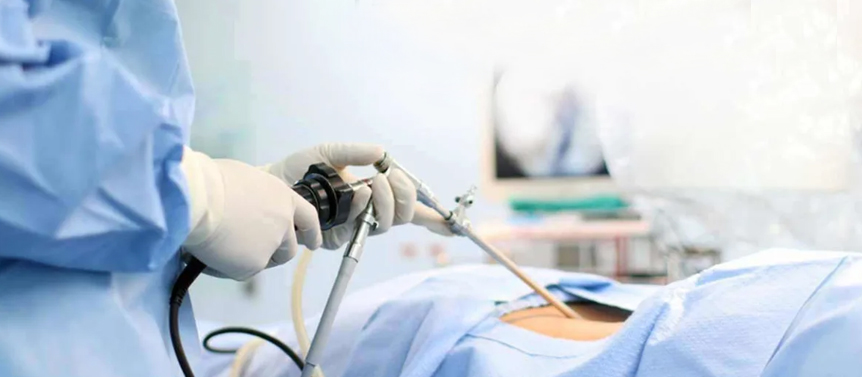
Endoscopic spine surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat various spinal conditions. It involves the use of an endoscope, a thin tube with a light and camera attached to it, which allows the surgeon to visualize and access the affected area of the spine through small incisions. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai.
During endoscopic spine surgery, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions, typically less than an inch in length, near the area being treated. The endoscope is then inserted through one of these incisions, providing a clear view of the spinal structures on a monitor. Additional small incisions may be made to introduce specialized surgical instruments, such as lasers or tiny surgical instruments, to perform the necessary procedures.
Endoscopic spine surgery can be used for various spinal conditions, including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, spinal tumors, and spinal deformities. Some common procedures performed using endoscopic techniques include:
- Discectomy: The surgeon removes a portion of a herniated or bulging disc that may be pressing on a nerve and causing pain or other symptoms.
- Foraminotomy: This procedure involves widening the foramen, the opening through which the spinal nerve exits the spinal canal, to relieve nerve compression.
- Facet joint surgery: The surgeon may use endoscopic techniques to treat facet joint arthritis or perform a facet rhizotomy to alleviate facet joint-related pain.
- Decompression procedures: Endoscopic techniques can be used to remove bone spurs, ligaments, or other tissues that may be compressing the spinal cord or nerves.
The benefits of endoscopic spine surgery include smaller incisions, reduced muscle damage, less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and potentially lower risk of complications compared to traditional open surgery. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
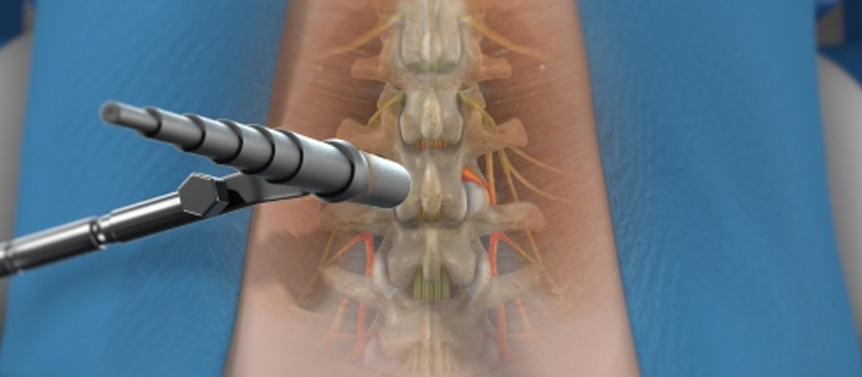
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is a surgical approach that aims to treat various spinal conditions while minimizing the damage to surrounding tissues. It utilizes advanced techniques and specialized instruments to perform spinal procedures through small incisions, resulting in reduced trauma, less blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and potentially faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
During minimally invasive spine surgery, the surgeon uses specialized instruments, such as tubular retractors, endoscopes, or robotic-assisted systems, to access the spine through small incisions. These instruments allow the surgeon to visualize and access the affected area of the spine without the need for large incisions or extensive muscle dissection.
Some common procedures performed using minimally invasive techniques include:
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of a herniated or bulging disc that may be pressing on a nerve and causing pain or other symptoms.
- Microdiscectomy: Similar to a discectomy, but it involves removing the herniated or damaged disc material using specialized microscopic instruments.
- Laminectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the lamina, which is the bony arch covering the spinal canal, to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Spinal fusion: Minimally invasive fusion techniques involve using screws, rods, or other implants to stabilize the spine and promote fusion between vertebrae. These procedures can be performed using small incisions and specialized techniques.
- Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: These procedures are used to treat vertebral compression fractures. They involve injecting bone cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize it and alleviate pain.
Minimally invasive spine surgery offers several potential benefits, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery, and smaller scars. However, not all patients or spinal conditions are suitable for this approach. The decision to undergo minimally invasive spine surgery is made on an individual basis, taking into account the patient's specific condition, medical history, and the expertise of the surgeon.
Spinal Fusion Surgery
Spinal fusion surgery is a surgical procedure performed to treat certain spinal conditions by joining two or more vertebrae together to create a solid bone fusion. The goal of spinal fusion is to stabilize the spine, reduce pain, and correct deformities or instabilities in the spinal column. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai.
During spinal fusion surgery, the surgeon typically uses bone grafts and implants, such as screws, rods, plates, or cages, to create the fusion. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision over the affected area of the spine. The size and location of the incision depend on the specific condition being treated.
- Preparation: The surgeon removes any damaged or degenerated discs, bone spurs, or other structures that may be causing pain or instability in the spine.
- Bone grafting: The surgeon places bone graft material between the vertebrae to promote bone growth and fusion. The graft can be obtained from different sources, including the patient's own bone (autograft), donor bone (allograft), or synthetic bone substitutes.
- Implants: In some cases, the surgeon may use implants, such as screws, rods, plates, or cages, to provide additional stability during the fusion process. These implants are typically made of metal and help hold the vertebrae in the correct position while the fusion occurs.
- Closure: The incision is closed using sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to the surgical site.
After spinal fusion surgery, the bone graft gradually fuses with the adjacent vertebrae over several months. This fusion eliminates motion at the fused segment and helps stabilize the spine. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai.
Recovery from spinal fusion surgery varies depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure. It often involves a hospital stay of a few days to a week, followed by a period of restricted activity and physical therapy. Pain management, monitoring for complications, and follow-up visits with the surgeon are important during the recovery period.
Spinal fusion surgery may be recommended for conditions such as spinal instability, degenerative disc disease, spinal deformities (e.g., scoliosis or kyphosis), spinal fractures, or certain types of spinal tumors. The decision to undergo spinal fusion surgery is made in consultation with a qualified spine surgeon or orthopedic surgeon who evaluates the patient's specific condition, symptoms, and imaging studies to determine the most appropriate treatment approach. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai.
Spinal Tuberculosis Surgery
Spinal tuberculosis, also known as Pott's disease, is a form of tuberculosis that affects the spine. It is a serious condition that can cause vertebral destruction, spinal deformities, and neurological complications if left untreated. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to manage the condition effectively.
The surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis aims to achieve several goals, including:
- Debridement and decompression: The surgeon removes the infected tissue, which may involve removing the affected vertebrae, discs, and nearby soft tissues. This helps to eliminate the source of infection and relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Stabilization and fusion: After the infected tissue is removed, the surgeon stabilizes the spine using implants such as screws, rods, plates, or cages. This helps to correct any deformities and prevent further collapse of the affected vertebral segments. Bone grafts may be used to promote fusion between the remaining healthy vertebrae.
- Reconstruction: In some cases, when significant bone and tissue loss occur, the surgeon may need to reconstruct the spine using bone grafts, bone cement, or other materials to restore stability and alignment.
The specific surgical technique and approach used for spinal tuberculosis surgery depend on factors such as the extent of the infection, the degree of vertebral collapse, and the presence of neurological complications. The surgery can be performed through traditional open techniques or minimally invasive approaches, depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's expertise.
Following surgery for spinal tuberculosis, patients typically require a prolonged period of anti-tuberculosis medication to treat the infection effectively. Rehabilitation and physical therapy are essential to regain strength, mobility, and functional abilities. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai
It's crucial to consult with a spine surgeon or orthopedic surgeon who specializes in spinal tuberculosis to assess the individual's condition, determine the appropriate surgical approach, and develop a comprehensive treatment plan. The surgeon will consider factors such as the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and the potential risks and benefits of surgery to make informed decisions regarding the management of spinal tuberculosis. Dr Dhiraj Sonawane is Surgeon for Spine Surgery in South Mumbai

