Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
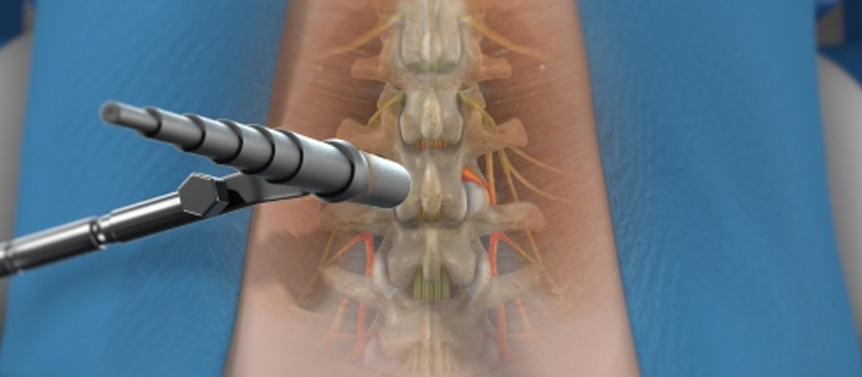
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is a surgical approach that aims to treat various spinal conditions while minimizing the damage to surrounding tissues. It utilizes advanced techniques and specialized instruments to perform spinal procedures through small incisions, resulting in reduced trauma, less blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and potentially faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
During minimally invasive spine surgery, the surgeon uses specialized instruments, such as tubular retractors, endoscopes, or robotic-assisted systems, to access the spine through small incisions. These instruments allow the surgeon to visualize and access the affected area of the spine without the need for large incisions or extensive muscle dissection.
Some common procedures performed using minimally invasive techniques include:
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of a herniated or bulging disc that may be pressing on a nerve and causing pain or other symptoms.
- Microdiscectomy: Similar to a discectomy, but it involves removing the herniated or damaged disc material using specialized microscopic instruments.
- Laminectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the lamina, which is the bony arch covering the spinal canal, to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Spinal fusion: Minimally invasive fusion techniques involve using screws, rods, or other implants to stabilize the spine and promote fusion between vertebrae. These procedures can be performed using small incisions and specialized techniques.
- Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: These procedures are used to treat vertebral compression fractures. They involve injecting bone cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize it and alleviate pain.
Minimally invasive spine surgery offers several potential benefits, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery, and smaller scars. However, not all patients or spinal conditions are suitable for this approach. The decision to undergo minimally invasive spine surgery is made on an individual basis, taking into account the patient's specific condition, medical history, and the expertise of the surgeon.

